Documents on cash transactions. Accounting for cash transactions and monetary documents at the enterprise
Any business transaction of an enterprise must be documented. Since (receiving and issuing money) also fall under this category, the legislation requires documentation cash transactions.
Procedure for processing cash transactions
This is written in detail in the Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions by legal entities and the simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions by individual entrepreneurs and small businesses.” In particular, it states that cash transactions must be formalized standard interdepartmental forms of primary accounting documentation for enterprises and organizations, which are approved by the State Statistics Committee of Russia and agreed upon with the Central Bank of Russia and the Ministry of Finance.
Required documentation and its completion
The State Statistics Committee of Russia has approved the following unified forms of primary accounting documentation (that is, documents with the help of which documentation is maintained):
- book of records accepted and issued by the cashier Money;
At the same time, individual entrepreneurs who keep records of income or income and expenses or physical indicators (in accordance with the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), may not draw up cash documents (receipt and expense orders).
Individual entrepreneurs are also exempt from maintaining a cash book. However, if an entrepreneur, in order to improve control over cash flow, decides to document cash transactions, he must follow the standards established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Let's take a closer look at what documents are used to document cash transactions (all of them are included in the All-Russian Classifier of Management Documentation OK 011-93).
Cash book
The cash book (number according to OK 0310004) is maintained to record the cash that arrives at the cash desk. Such a book can be kept both in paper and electronic form.
If a book is kept on paper, all its sheets must be numbered before making entries; the paper fastening the sheets must be signed by the chief accountant and manager. Also, the book must be certified by the seal of an individual entrepreneur (if he has one).
If the book is maintained in electronic form, measures must be taken to ensure that the information cannot be changed or falsified.
Entries in such a book are certified by electronic digital signatures of authorized persons, and the decision on the timing of printing information (daily, once a week or quarter, etc.) is made by the manager.
Page numbering must also be carried out in the electronic version of the cash book, and it is carried out automatically and in chronological order. Printed copies of the cash book sheets must be collected in a separate folder - this can be done to the extent possible or desired, but the book must be collected within one calendar year.
Entries in the cash book are made by the cashier based on receipts and expenditure orders- only for those funds that went directly to the cash desk. Cash accepted by a paying agent or banking subagent is recorded in separate cash books maintained directly by the agents themselves.
At the end of each working day, the cashier must check the cash book data with the data in cash documents and record the amount of cash balance with his signature. After this, the data is reconciled by the chief accountant or manager (in the absence of an accountant) and also signed.
If on any day or even days no cash transactions were made, the balance does not need to be withdrawn each time: the amount of the balance will be considered the last one withdrawn on the day when the transactions were made.
Control over the maintenance of the cash book is carried out by the chief accountant of the enterprise. In his absence, control is exercised by the head of the enterprise.
Let us note once again that from June 1, 2014, an entrepreneur is not obliged, but can do this to organize control and.
Receipt order
(PKO) has, according to the General Classifier, number 0310001 and documents the execution of cash transactions (receipt of cash at the cash desk). The order can be filled out either manually or on a computer or typewriter; blots and corrections are not allowed.
In addition to the registration number, the order must have the following details:
- name of the enterprise, structural unit (if necessary) indicating OKPO codes;
- date of completion;
- number of the corresponding account or subaccount (for accounting purposes).
The cashier is obliged to check the information in the receipt order (for accuracy and completeness), as well as the attached documents.
Withdrawal slip

 Expenditure (RKO) has, according to the General Classifier, number 0310002 and is used to register the issuance of funds from the cash register.
Expenditure (RKO) has, according to the General Classifier, number 0310002 and is used to register the issuance of funds from the cash register.
The details of the expenditure order are the same as those of the receipt order; in addition, it must be certified by the chief accountant and signed by the manager (or his authorized person).
When issuing funds, the cashier must check the recipient’s receipt (filled out only in the recipient’s own handwriting, the amount of rubles is indicated in words, kopecks in numbers) and an identity document (within the enterprise this can be an ID). The cashier must write down the document details.
If funds are issued by power of attorney, the name of the authorized person is indicated in the order after the name of the recipient. If funds are issued according to a statement, before the receipt of the money, the cashier must write “By power of attorney.” The power of attorney is attached to the order or statement.
Cash book
The cash book is kept by the senior cashier to document cash transactions between him and the other cashiers during the working day (for small-scale businesses there is no need for such a book).
OK book code is 0310005.
At the beginning of the working day, the chief accountant issues cash to the required circle of people against signature in the book, at the end of the working day the balance of funds is also handed over against signature.
If funds are issued to pay wages, you must report for them before the end of the deadline indicated on the payroll.
The balance of undistributed money is sealed daily in an envelope indicating the exact amount and handed over to the chief accountant against receipt. If, after the expiration of the period indicated in the payroll, some amount remains, it is returned to the central cash desk, and a corresponding entry is made in the book.
Payroll
This document is maintained to record time worked, accruals, deductions and payments to employees of the enterprise. The General Classifier code is 0301009.
The statement is compiled by the accounting department in one copy based on primary documents for recording production, actual time worked, and the like. If employees receive wages for bank cards, only a payslip is prepared.
The statement indicates all the amounts required to be paid to the employee: wages, social benefits, allowances and bonuses (as well as deductions and deductions). The total amount of payments is indicated on the title page.
Opposite the names of those employees whose wages have not been paid for some reason, “deposited” is indicated. In the last column of the statement, the total amount of payments is entered, cash settlements are made for it, and the number and date of the order are recorded in the statement.
It should be noted that when issuing wages and other payments to employees in cash, the entrepreneur is required to generate payroll (or payroll) statements.
Payment statement
Maintained to record the payment of wages and other payments to employees. The code according to the General Classifier is 0301011. It is drawn up in the same way as the settlement and payment (settlement) statement.
Wages can also be paid to employees using an expense order, but it is wiser to keep records in a statement.
General documentation of cash transactions is carried out by the chief accountant (or the person replacing him) or the manager. Corrections in documents are not allowed.
What's new in 2017
2017 provides an opportunity for small businesses not to set cash limits in their cash registers: they can accumulate the necessary amounts without breaking the law.
In the new year, all cash documents remain the same, as well as the form of their submission:
- in paper form;
- through electronic systems.
In general, no major changes are planned for 2017. An innovation could be the adoption of a Federal Law on changes in the use of cash registers, as well as changes to the Code of Administrative Violations. The draft law has yet to be developed, but experts say there is a high probability of its adoption.
The law will make the following changes:
- mandatory transfer of cash receipts to product buyers;
- during the purchase, the receipt will also be generated electronically;
- a cash document compiled in this way will be automatically sent online to the tax office;
- upon a separate request from the buyer, the entrepreneur will have to send a duplicate of the check to email specified by the client.
If this bill is passed, all entrepreneurs will have to replace equipment or software.
Sending information will need to be done through data operators accredited by the fiscal authorities. For violation of the procedure for submitting reports or the deadlines for their submission, an administrative penalty will be imposed on the violator. To give entrepreneurs time to make the transition to new equipment, the bill plans to establish a transition period of at least 5 years. During this time, all persons subject to the regulation must purchase equipment, configure it, and install software.
Control of cash transactions: Video
Each business transaction of an enterprise must have documentary evidence.
Cash transactions, namely, the receipt and issuance of money fall under this category, therefore the law requires the documentation of all cash transactions.
This is described in detail in the Regulations on the “Procedure for conducting cash transactions with banknotes and coins of the Bank of Russia in the territory Russian Federation» dated October 12, 2011 No. 373-P of the Central Bank (hereinafter referred to as the Regulations).
There, in particular, it is stated that enterprises must formalize cash transactions using standard interdepartmental forms of primary accounting documentation for enterprises and organizations, approved by the State Statistics Committee of Russia and agreed upon with the Ministry of Finance and the Central Bank of Russia.
The State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation has approved unified forms of primary accounting documentation. These are documents with the help of which documentation of cash transactions carried out at the enterprise should be maintained:
- withdrawal slip
- receipt order
- payroll
- book of accounting of funds accepted and issued by the cashier
- payment statement.
Let us dwell in a little more detail on the documents that must be used to formalize cash transactions of an enterprise. All of them are reflected in the All-Russian Classifier of Management Documentation OK 011-93.
Cash book
 Cash book (OK 0310004) is a document that keeps records of cash received at the cash desk of an enterprise.
Cash book (OK 0310004) is a document that keeps records of cash received at the cash desk of an enterprise.
The (fifth) section of the Regulations is completely devoted to this topic - the correct maintenance of the cash book. It is noted there that the cash book can be maintained both in paper form and electronically. .
In the case of traditional bookkeeping, i.e. on paper, all sheets of the document must be numbered before recording begins.
The binding paper must be signed by the chief accountant and the head of the enterprise. It must also be certified by the seal of the organization or individual entrepreneur (if any).
If the book is kept in electronic form, then all possible measures must be taken to ensure that the information in the book cannot be changed or falsified.
Entries in such a book must be certified by digital electronic signatures of authorized persons. The decision on the timing of when information needs to be printed (once a day, weekly, quarterly, etc.) is made by the manager.
It should be taken into account that in the event of an external audit, the cash book will have to be printed.
Page numbering is also carried out in the electronic version of the book; in this case, it appears automatically, in chronological order.
Copies of printed sheets of the cash book must be collected in a separate folder. It is better to do this as much as desired or possible, but do not delay it: the book must be collected within a calendar year.
Entries in the cash book must be made by the cashier, receiving receipts and expenditure orders, and only for those funds that go directly to the cash desk.
Cash accepted by a bank subagent or paying agent is recorded in those cash books that the agents themselves are required to maintain.
At the end of each working day, the cashier is obliged to check the book data with the data of all cash documents and record the balance of cash with his signature. Next, the data is reconciled either by the chief accountant or the head of the enterprise (if there is no accountant) and also signs.
If on one day or even several days not a single cash transaction is made, then the balance does not need to be withdrawn each time, since the amount of the balance can be considered as withdrawn on the last day when cash transactions were made.
If the cash book is not maintained by a senior cashier, but simply by a cashier (or an employee replacing him) of a department, then after the balance of cash is withdrawn, this sheet of the cash book is transferred to the manager. In the case when the book exists in paper form, a tear-off sheet must be transmitted, if the book is electronic, a printout must be submitted.
The maintenance of the cash book is controlled by the chief accountant of the enterprise, and in his absence - by the manager.
Receipt order
PKO - cash receipt order according to the General Classifier has number 0310001 and is used for documentation all cash transactions, that is, the receipt of cash at the cash desk.
The order is filled out manually and on a computer or typewriter. Corrections and erasures are not permitted under any circumstances. . In addition to the registration number, the order must have the following details:
- name of the organization or structural unit
- indicating its codes and structural unit according to OKPO
- Date of completion
- subaccount or corresponding account number.
The cashier must check all the information contained in the receipt order for the completeness and correctness of all attached documents.
Withdrawal slip
RKO - expenditure cash order according to the General Classifier has number 0310002 and is necessary for processing the issuance of funds from the enterprise's cash desk.
The details of the expense order do not differ from the details of the receipt note; it must be certified by the chief accountant of the enterprise and signed either by the manager or a person authorized by the manager.
The cashier, when issuing funds, is obliged to check the recipient’s receipt, which is filled out only by the recipient, and where the amount of rubles must be indicated in words, and kopecks in numbers. You also need a document confirming your identity (it can even be an identity card), as well as the details of the document.
If money is issued by power of attorney, the name of the authorized person must be indicated in the order after the full name of the recipient. When issuing funds according to a statement, before signing a receipt for receipt, the cashier must make the appropriate mark - “By power of attorney.” The power of attorney itself is attached to the order or statement.
Book of accounting of funds accepted and issued by the cashier
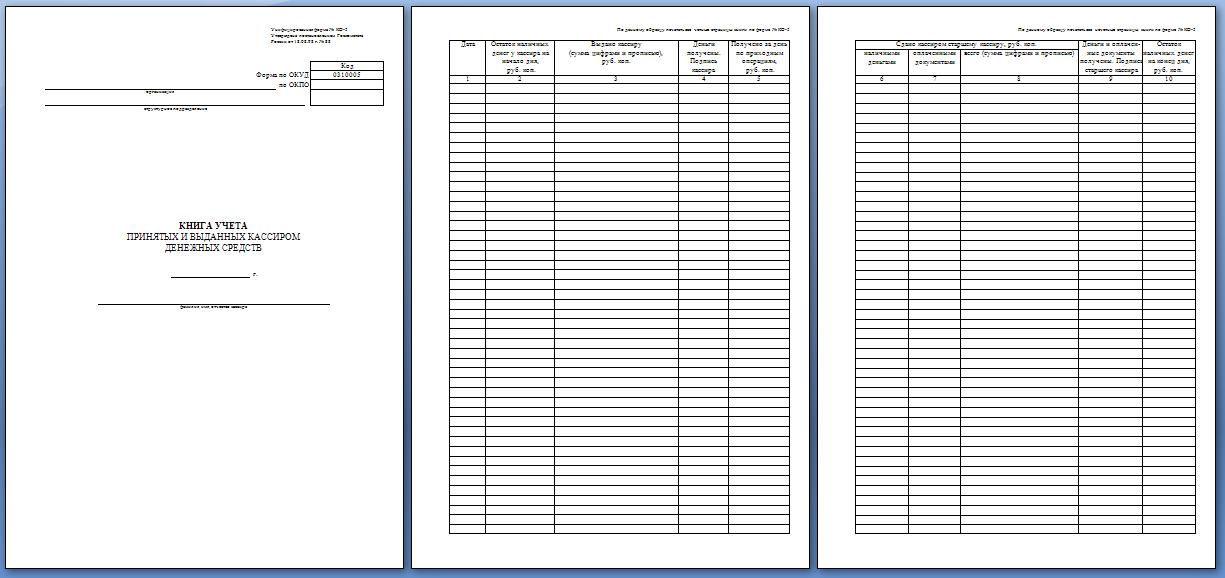
Registration of cash transactions
The fund accounting book must be maintained by the senior cashier, and is intended to document cash transactions that occur between the senior cashier of the enterprise and the rest of the cashiers during the working day. Such records are kept only at large enterprises; in a small company there is simply no need for such a book. Book code according to OK 0310005.
At the beginning of each working day, the chief accountant issues cash to the required circle of people against signature in the book, and at the end of the work the balance of funds is handed over against signature.
If funds are issued to pay salaries, you must report for them before the end of the period indicated on the payroll. The balance of money is sealed daily in an envelope with an exact indication of the amount, and is handed over to the chief accountant against receipt. If, at the end of the period noted in the payroll, some amount remains, then it must be returned to the central cash office.
Payroll
This is a document that takes into account the time worked, accruals, deductions and payments to employees of the enterprise. According to the general classifier - code 0301009.
The statement is compiled in the accounting department in a single copy on the basis of primary documents recording actual time worked, output, etc.
If employees have their wages transferred to bank cards, then only a payslip is prepared.
This statement must indicate the amounts required to be paid to the employee: these are wages, allowances and bonuses, social benefits, as well as all deductions and deductions . The total amount is reflected on the title page.
If for some reason employees have not been paid their salaries at the end of a certain period, the accountant makes a note “deposited”. The last column of the statement contains information about the total amount of payments, and cash settlements are compiled for it. The number and date of the order are recorded in the statement
Payment statement
This document is maintained to record the payment of salaries and other payments to employees of the enterprise. According to the general classifier - code 0301011.
The statement is prepared in the same way as the settlement and payment statement. Wages are sometimes paid to employees using a cash receipt, however, it is wiser to keep such records in a statement.
All documentation of cash transactions is carried out by the chief accountant (or his replacement) or by the manager. Corrections in documents are not allowed.
assistant manager
on taxes
LLC "Ramses"
IN Lately Electronic technologies are increasingly becoming part of our lives. According to the strategy for the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation for the period until 2030 (Order No. 1083-r dated June 2, 2016), it is planned to make a gradual transition to the use of software that allows data to be transferred in electronic form. Therefore, soon, apparently, companies and entrepreneurs will be forced to use new cash register equipment with the transfer of data to the tax authority.
The main document regulating the execution of cash transactions is the Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U (as amended on February 3, 2015) “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions by legal entities and the simplified procedure for conducting cash transactions by individual entrepreneurs and small businesses.”
GOOD TO KNOW
Cash transactions can be carried out by the manager.
Cash documents are prepared:
- chief accountant;
- an accountant or other official (including a cashier) specified in an administrative document, or an official legal entity, an individual with whom contracts have been concluded for the provision of accounting services (hereinafter referred to as the accountant);
- manager (in the absence of a chief accountant and accountant).
The cashier accepts cash by sheet, piece by piece.
Cash is accepted by the cashier in such a way that the cash depositor can observe the actions of the cashier.
Documents can be prepared on paper or electronically.
GOOD TO KNOW
A legal entity or individual entrepreneur can conduct cash transactions using software and hardware.
Cash receipt
Mandatory details of a cash receipt include:
1) name and TIN of your organization;
2) serial number of the cash register;
3) serial number of the check;
4) date and time of purchase (service provision);
5) the cost of the purchase (service), while the amount of VAT may not be indicated;
6) a sign of the fiscal regime.
Example 1.

The presence of the necessary details in the cash receipt is checked when registering a cash register with the Federal Tax Service. Due to their absence, registration of a cash register may be refused (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated March 6, 2013 No. AS-4-2/3777).
GOOD TO KNOW
Other documents drawn up when conducting cash transactions should be distinguished from cash documents:
- cash book;
- book of accounting of funds accepted and issued by the cashier;
- supporting documents (payment slips, pay slips, statements, invoices, other documents), etc.
Sales receipt, receipt or other document confirming receipt of funds for the relevant product (work, service)
This document is issued at the time of payment for goods (work, services) and must contain the following information:
- Title of the document;
- serial number of the document, date of issue;
- name - for an organization (last name, first name, patronymic - for an individual entrepreneur);
- taxpayer identification number assigned to the organization ( individual entrepreneur), who issued (issued) the document;
- name and quantity of paid goods purchased (work performed, services rendered);
- the amount of payment made in cash and/or using a payment card, in rubles;
- position, surname and initials of the person who issued the document, and his personal signature.
The sales receipt form has not been officially approved, so taxpayers can develop it independently (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 30, 2011 No. 03-11-11/107).
Example 2.

It is possible to replace cash register receipts with sales receipts, for example, by combining the tax regimes of UTII and the simplified tax system in terms of the application of a single tax on imputed income.
GOOD TO KNOW
Primary accounting documents and appendices to them, which recorded the fact of a business transaction and served as the basis for accounting records (including cash documents and books, orders, advance reports), are subject to storage for five years.
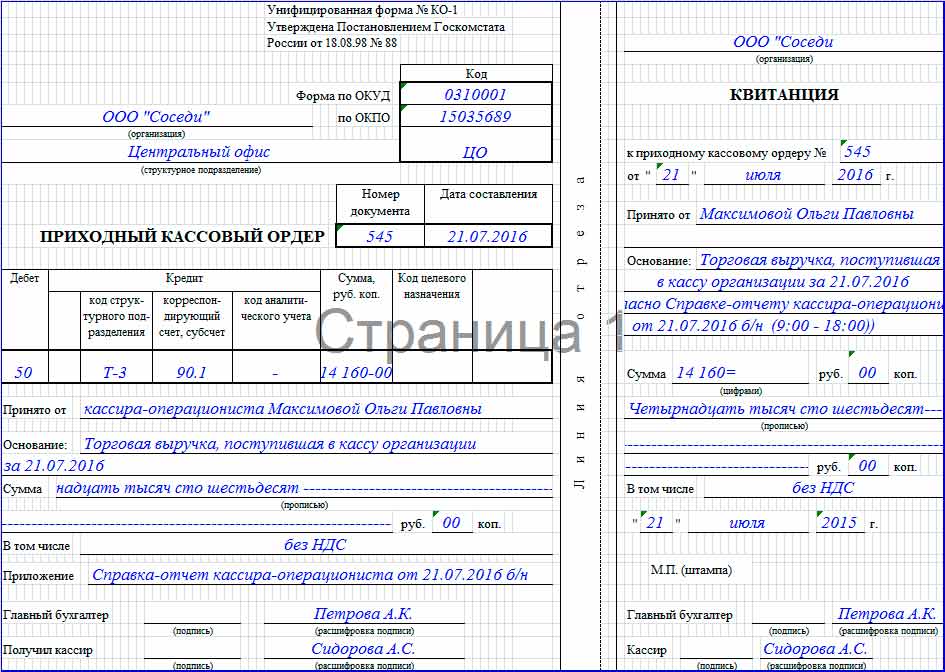
Receipt cash order
The receipt of funds can be documented by a cash receipt order. Its form is established by law - form KO-1.
Since the cash receipt order was established by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88 (as amended on May 3, 2000) “On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for recording cash transactions and recording inventory results,” then, accordingly, invent and develop its form is not required, and all details are established in the form developed by law.
A cash receipt order is issued when registering revenue to the enterprise's cash desk. When selling goods (work, services) for cash, when the buyer is given a cash register receipt, at the end of the work shift, one cash receipt order is drawn up for the entire amount of cash proceeds (clause 5.2, clause 5 of Directive No. 3210-U, clause 3 of the letter Federal Tax Service dated 07/09/2014 No. ED-4-2/13338).
The cash receipt order is issued in one copy by an accounting employee and signed by the chief accountant or a person authorized to do so.
The receipt for the cash receipt order is signed by the chief accountant or a person authorized to do so, and the cashier, certified by the cashier’s seal (stamp), registered in the register of receipts and expenditure cash documents (Form No. KO-3) and handed over to the person who deposited the money, and the receipt the cash order remains in the cash register.
Let's give an example of the design.
Account cash warrant
Expense cash orders are issued in cases where it is necessary to issue funds from the cash register. In practice, there are quite a lot of such cases (for example, in the case of payment of wages not on a card, but by issuing them through the cash register to an employee, or in the case where it is necessary to purchase stationery and the funds are issued on account to the employee).
The form of the cash settlement order was also approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88, therefore there are no mandatory details for this form. The expenditure order is drawn up in the KO-2 form. In this case, an expense cash order is used to formalize the issuance of cash from the organization’s cash desk; its form requires the mandatory indication of the surname, first name, patronymic of the recipient of the funds and details of the identity document (resolution Supreme Court RF dated June 15, 2015 No. 25-AD15-3).
An expense cash order is issued in one copy by an accounting employee, signed by the head of the organization and the chief accountant or a person authorized to do so, and registered in the register of receipts and expenses cash documents (Form No. KO-3).
POSITION OF THE BANK OF RUSSIA
If workplace accountant is geographically remote from the cash desk, cash documents can be prepared by the accountant electronically using an electronic signature and transferred to the cashier for printing on paper. Obviously, the chief accountant and the manager also have the right to draw up cash documents electronically. The cashier puts a signature and a seal (stamp) on the printed document.
Registration of cash documents in electronic form
Currently, there is no obligation to prepare cash documents electronically. However, since 2014, it has become possible to prepare documents in electronic format. What is the convenience of filing documents electronically?
Firstly, this speeds up settlements between the parties.
Secondly, checks, receipts, cash book and salary slips remain in electronic form and in the event of a controversial situation they can always be used as evidence.
The requirements for the execution of cash documents in electronic form are established in the Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U. The features of document execution in electronic form include the following:
1. Electronic cash documents can be processed and stored electronically without printing. An order for the transfer of valuables that does not contain the signature of the client (depositor, recipient), a foreign currency cash order, a turnover sheet, a balance sheet, a book of registration of open accounts can now be stored in electronic form (Instruction of the Bank of Russia dated December 8, 2014 No. 3472-U).
However, in some cases, documents need to be printed. Such cases include the need to print out cash receipts, cash outflows, and salary slips.
What risks arise if the company does not print the documents? If the tax authorities notice the fact of non-printing tax audit, then they can fine the organization (businessman) for violating the procedure for conducting cash transactions and not posting revenue.
Fine for companies - up to 50,000 rubles, for businessmen - up to 5,000 rubles. (Articles 2.4 and 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). The fine can only be canceled in court (resolutions of the FAS Moscow District dated March 11, 2009 No. KA-A40/1416-089 and FAS Volga District dated March 17, 2010 No. A12-19131/2009).
GOOD TO KNOW
Documents in electronic form are drawn up using technical means that ensure their protection from unauthorized access, distortion and loss of information, and are signed with electronic signatures in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law dated 04/06/2011 No. 63-FZ. It is not allowed to make corrections to documents executed electronically after they have been signed.
2. Documents in electronic form are drawn up using technical means, taking into account their protection from unauthorized access, distortion and loss of information. But regarding the signing of such documents, questions may arise regarding the use of the signature.
In accordance with Part 2 of Art. 6 of Law No. 63-FZ, information in electronic form, signed with a simple electronic signature or a non-qualified electronic signature, is recognized as an electronic document equivalent to a paper document signed with a handwritten signature, in cases established by federal laws, normative legal acts adopted in accordance with them or agreement between participants in electronic interaction. Regulatory legal acts and agreements between participants in electronic interaction that establish cases of recognizing electronic documents signed with a non-qualified electronic signature as equivalent to paper documents signed with a handwritten signature must provide for a procedure for verifying an electronic signature.
Thus, if there is a legally valid agreement, business parties can organize electronic document flow using a simple and/or enhanced unqualified electronic signature (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 17, 2014 No. PA-4-6/489).
3. Documents in electronic form are drawn up using technical means, taking into account their protection from unauthorized access, distortion and loss of information. Documents executed in electronic form are signed with electronic signatures in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law dated 04/06/2011 No. 63-FZ “On Electronic Signatures”.
4. Corrections are not allowed in electronic cash documents.
5. According to the Directive of the Bank of Russia dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U, cash documents are drawn up by the chief accountant or accountant (in their absence, by the manager) and signed by the chief accountant or accountant (in their absence, by the manager), as well as by the cashier. In this case, the term “accountant” means an accountant or other official (including a cashier) defined in an administrative document, or an official of a legal entity, individual, with whom agreements have been concluded for the provision of accounting services.
GOOD TO KNOW
The execution of cash documents in electronic form means their filling out using software and hardware. In this case, we are not talking about drawing up a document on a computer and printing it (it will still be a paper document), but about a completely electronic form. That is, an electronic cash document is a document filled out only on a computer using a program and signed with an electronic signature.
6. There are features of simultaneously registering an electronic document (for example, a ticket),
and an electronic cash document (for example, a check).
Clause 2 of the order of the Ministry of Transport of Russia dated November 8, 2006 No. 134 and clause 2 of the order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated August 21, 2012 No. 322 clearly states that the route/receipt and control coupon are strict reporting forms. Forms of electronic tickets, as well as details of the route/receipt and control coupon are approved by the Ministry of Transport of Russia in accordance with clause 5 of the Regulations approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2008 No. 359. Consequently, such documents are equivalent to checks of cash register equipment for the purpose of confirming the fact of settlements using cash or payment cards.
In conclusion, it should be noted that in the case of a transition to cash documents in electronic form, it is advisable to consolidate such a transition in the company’s accounting policy, in particular, it is necessary to indicate which documents are used in electronic form, how they are stored and what features of use are typical for the contract organization.
Access to full texts articles are available by subscription. Several articles in each issue are publicly available. You can also get one of the magazine's issues for free. If you liked our magazine, information on subscription can be obtained. Here is a list of subscriptions that allow you to read this article:
Preparation of cash documents by the cashier
Cashier upon receipt of cash receipts and debit orders or documents replacing them:
– checks the presence and authenticity of the signature of the chief accountant on the documents, and on the cash receipt order or a document replacing it - the authorization inscription (signature) of the head of the enterprise or persons authorized to do so;
– checks the correctness of documents;
– checks the presence of the applications listed in the documents.
If one of these requirements is not met, the cashier returns the documents to the accountant for proper processing.
If all the above requirements are met and the documents match, the cashier accepts cash. When accepting cash, the cashier checks its solvency in accordance with the Signs of solvency of banknotes and the Rules for the exchange of banknotes and coins of the Bank of Russia, approved by the instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2006 No. 1778-U, and the Regulations on the procedure for conducting cash transactions and the rules of storage and transportation and collection of banknotes and coins of the Bank of Russia in credit institutions on the territory of the Russian Federation, approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on April 24, 2008 No. 318-P.
The amount received by the cashier must correspond to the amount indicated in the cash receipt order.
After accepting the money, the cashier signs the receipt and deciphers the signature (puts the surname and initials), certifies it with the cashier’s seal (stamp). A receipt for a cash receipt order, signed by the chief accountant and a person authorized to do so, and by the cashier, certified by the cashier’s seal (stamp) or imprint cash register, issued to the person who handed over the money.
Receipt cash orders or documents replacing them are immediately signed by the cashier after receiving or issuing money on them, and the documents attached to them are canceled with a stamp or handwritten inscription “Paid” indicating the date (day, month, year).
Cash not confirmed by receipts cash orders, are considered cash surplus and are included in the income of the enterprise.
In accordance with clause 14 of the Procedure for conducting cash transactions in the Russian Federation, the issuance of cash from the cash registers of enterprises is carried out according to cash outflow orders (form No. KO-2) or properly executed other documents (pay slips (settlement and payment), applications for the issuance of money, accounts, etc.) with the imposition of a stamp on these documents with the details of the cash receipt order.
The issuance of money to persons who are not on the payroll of the enterprise is carried out according to cash receipts issued separately for each person, or according to a separate statement based on concluded agreements.
Documents for the issuance of money must be signed by the manager, chief accountant of the enterprise or persons authorized to do so. In cases where documents, statements, invoices, etc., attached to cash receipts. There is a permit from the head of the enterprise; a signature on cash receipts is not required.
If all the above requirements are met and the documents match, the cashier issues cash.
When issuing money according to an expense cash order or a document replacing it to an individual, the cashier:
– requires the presentation of a document (passport or other document) identifying the recipient. At an enterprise, money can be issued using a certificate issued by this enterprise, if it contains a photograph and personal signature of the owner. The cashier issues money only to the person indicated in the cash receipt order or a document replacing it. If the issuance of money is made by power of attorney, executed in the prescribed manner, in the text of the order after the last name, first name and patronymic of the recipient of the money, the accounting department indicates the last name, first name and patronymic of the person entrusted with receiving the money. The power of attorney remains in the documents of the day as an attachment to the cash receipt order;
– records the name and number of the document, by whom and when it was issued and selects the recipient’s receipt. A receipt for receipt of money can only be made by the recipient personally in ink or with a ballpoint pen indicating the amount received: rubles - in words, kopecks - in numbers;
– gives money to the recipient.
Upon completion of the operation, the cashier is required to sign the cash receipts, and pay off the expense documents attached to them with a stamp or the inscription: “Paid” indicating the date, month and year.
Payment of labor, payment of social insurance benefits and scholarships are made by the cashier according to payroll (settlement and payment) statements without drawing up an expense cash order for each recipient.
On the title page of the payment (settlement and payment) statement, an authorization inscription on the issuance of money is made, signed by the head and chief accountant of the enterprise or persons authorized to do so.
A similar procedure can be used to formalize one-time payments of money for wages (when going on vacation, sickness, etc.), as well as the issuance of deposited amounts and money on account for expenses associated with business trips to several persons.
One-time payments of money for wages to individuals are made, as a rule, but on expense cash orders.
Issuance of money to persons involved in agricultural and loading and unloading work, as well as for liquidation of consequences natural Disasters, can be made according to the statement. The statements are compiled separately for each organization whose employees were sent to the specified work, and are certified, in addition to the signature of the head and chief accountant of the enterprise - the organizer of the work, with the signature of the authorized representative of the relevant organization.
If the issuance of money is carried out by power of attorney, executed in the prescribed manner, in the statement, before the receipt for receipt of money, the cashier makes the inscription: “By power of attorney.” The power of attorney remains in the documents of the day as an appendix to the statement.
Upon expiration of the established deadlines for payment of wages, payment of social insurance benefits and scholarships (no more than three working days), the cashier must:
– in the payroll (settlement and payment) statement, check the wages issued line by line and against the names of persons to whom the specified payments have not been made, in the “receipt receipt” column, put a stamp or make a handwritten note: “Deposited”. Unreceived wages must be deposited after the five days established for the payment of wages;
– close the payroll (settlement and payment) statement with two amounts: at the end of the statement you must make an inscription about the amounts actually paid and deposited, check them with the total for the payroll and seal the inscription with your signature. If the money was issued not by the cashier, but by another person, then an additional inscription is made on the statement: “I issued the money according to the statement (signature). The issuance of money by the cashier and the distributor on the same statement is prohibited;
– transfer the payroll and the register of unpaid wages to the accounting department for verification and issuance of a cash receipt for the amount issued;
– record the amount actually paid in the cash book and put a stamp on the statement: “Cash expenditure order No. _______.”
The accounting department checks the marks made by the cashier in the payment (settlement and payment) statements and calculates the amounts issued and deposited on them and transfers the cash receipt order to the cashier for registration in the cash book.
The cashier submits the amounts of unclaimed wages to the bank to the company's current account with the indication: "Deposited amounts." The bank must take into account these amounts separately, since they can be claimed at any day, they cannot be used for other payments to the enterprise (repayment of debts, etc.). For the deposited amounts handed over to the bank, one general cash outgoing order is drawn up.
No erasures, blots or corrections are allowed in cash documents.
Money on cash orders is issued only on the day these documents are drawn up. Expense cash orders or documents replacing them are not issued to persons receiving money.
The issuance of money from the cash register, which is not confirmed by the recipient's receipt in the cash receipt order or other document replacing it, is not accepted to justify the balance of cash in the cash register. This amount is considered a shortage and is collected from the cashier.
At enterprises with a large number of divisions served by central cash desks, payment of taxes and payments of social insurance benefits can be made by several cashiers or proxies (distributors). In this case, the chief (senior) cashier, before the start of the working day, gives the other cashiers in advance the necessary expense transactions the amount of cash against a receipt in the book of accounting of funds accepted and issued by the cashier (form No. KO-5).
Cashiers (distributors) at the end of the working day are required to report to the chief (senior) cashier in the amounts received and hand over the balance of cash to him against a receipt in the book of accounting for funds accepted and issued by the cashier.
For advances received for wages and scholarships, the cashier is obliged to report within the period specified in the payroll for their payment. Before the expiration of this period, cashiers (distributors) are required to hand over to the cash desk daily the balance of cash not issued according to pay slips. This money is handed over in bags, packages and other packaging sealed by cashiers to the chief (senior) cashier against a receipt indicating the declared amount.
Maintaining a cash book
The cashier's responsibilities include maintaining a cash book (Form No. KO-4). All cash receipts and disbursements of the enterprise are recorded in the cash book. The company maintains only one cash book. Entries in the cash book are kept in two copies.
Each sheet of the cash book consists of two equal parts: one of them (with a horizontal ruler) is filled out by the cashier as the first copy, the second (without horizontal rulers) is filled out by the cashier as the second copy from the front and back through carbon paper. First, the sheet is folded along the cut line, placing the tear-off part of the sheet under the part of the sheet that remains in the book. To keep records after the “Transfer”, the tear-off part of the sheet is placed on the front side of the continuous part of the sheet and records are continued along the horizontal rulers of the reverse side of the continuous part of the sheet.
The first copies of sheets remain in the cash book. The second copies of the sheets must be tear-off, they serve as the cashier’s report and are not torn off until the end of operations for the day.
The first and second copies of sheets are numbered with the same numbers.
Erasures and unspecified corrections in the cash book are not permitted. The corrections made are certified by the signatures of the cashier, as well as the chief accountant of the enterprise or the person replacing him.
Entries in the cash book are made by the cashier immediately after receiving or issuing money for each order or other document replacing it.
Every day at the end of the working day, the cashier calculates the results of transactions for the day, displays the balance of money in the cash register for the next date and transfers to the accounting department as a cashier’s report a second tear-off sheet (a copy of the entries in the cash book for the day) with receipts and expenses cash documents against receipt in the cash register book. Control over the correct maintenance of the cash book rests with the chief accountant of the enterprise.
All funds that appear in enterprises leading economic activity and those receiving profit from this (including individual entrepreneurs) must be kept in a bank account.
But there are situations in which some of the money remains with the business entity and is used for certain purposes (for example, issuing wages or travel allowances). For this purpose, there is a cash desk of the organization, where strict records of received and issued financial resources are kept.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
(Moscow)
(Saint Petersburg)
(Regions)
It's fast and for free!
What is it regulated by?
 Accounting for the movement of inventory items of an entity that conducts business activities, which includes cash, securities, as well as other documents giving the right to receive finance for them, is on special control at special bodies(tax inspectorates), since they are the basis for taxation.
Accounting for the movement of inventory items of an entity that conducts business activities, which includes cash, securities, as well as other documents giving the right to receive finance for them, is on special control at special bodies(tax inspectorates), since they are the basis for taxation.
Therefore, the rules for such accounting are clearly stated in various regulatory legal acts of our state. These include the following legislative norms:
- Regulations on the rules for organizing cash circulation on the territory of the Russian Federation, which was approved on January 5, 1998 under number 14-p.
- Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998, number 88, which approved unified forms of primary accounting documentation.
- in the Russian Federation, which was adopted by the decision of the Board of Directors of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on September 22, 1993 under number 40.
The first normative act establishes general rules circulation of cash and obliges all organizations that conduct business activities to store their cash in banking institutions in special commercial accounts. It also states that the company may keep some of the money in cash.
For these purposes, the management of such a structure, together with the servicing bank, establishes by mutual agreement.
The limit means the maximum amount of money and securities with a nominal value that can remain in the cash register at the end of the working day and not be handed over to a banking institution. Exceeding this amount entails the imposition of penalties on the enterprise or individual entrepreneur. Non-compliance with the established limit is allowed only on the day of payment of salaries and other social payments to employees of the organization.
 The second normative act establishes samples of cash documentation, the procedure for maintaining and filling them out. The third act regulates the process of conducting cash transactions, and also approves a list of documents (cash orders, books, pay slips) that confirm the performance of certain actions with money (financial transactions) that are in the cash register.
The second normative act establishes samples of cash documentation, the procedure for maintaining and filling them out. The third act regulates the process of conducting cash transactions, and also approves a list of documents (cash orders, books, pay slips) that confirm the performance of certain actions with money (financial transactions) that are in the cash register.
It is important to know that the receipt and withdrawal of funds from the cash register relate to transactions confirming the economic activities of an enterprise or individual entrepreneur. All this is documented with receipt and expense documents. All primary financial (accounting) accounting is carried out on their basis.
Types of cash documents
Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998, number 88, which approved unified forms of primary accounting documentation, establishes the following cash documents:
- (form KO-1). It accepts all cash, as well as securities that come to the cash desk.
- (form KO-2). It issues financial resources, as well as securities from the cash register.
- A journal in which all incoming and outgoing orders are recorded ().
- The cash transactions book (), which reflects all cash movements and also records their balance at the end of the working day (form KO-4).
- A book that displays records of all financial resources issued and received by the cashier of an enterprise or individual entrepreneur ().
 In some cases, the cashier may issue wages, stipends, and other payments on statements. They are either . Despite some differences in the name, legally these are the same financial document, which has mandatory details to fill out.
In some cases, the cashier may issue wages, stipends, and other payments on statements. They are either . Despite some differences in the name, legally these are the same financial document, which has mandatory details to fill out.
It should be noted that in cash orders, according to which funds are received and issued, any corrections are prohibited, erasures. If these documents were initially drawn up incorrectly, then they are written off by the act and new ones are drawn up.
Documentation of transactions
All transactions with finances and other securities that have a cash equivalent (for example, traveler's checks, stamps) are executed by cash orders. The latter, in turn, are recorded in the order journal, and the funds (their amounts) are entered into the cash book.
Transactions involving the receipt of money at the cash desk are documented using cash receipt orders (PKO).
The requirements for their preparation are as follows:
- the date of compilation must correspond to the day of the operation;
- personal information and position of the person who issued the warrant are required;
- the reasons for their preparation must be indicated (return of unused travel funds, payment for goods or services provided);
- it is necessary to indicate the details of the documents attached and confirming the operation (date, number, name).
You should immediately note that the regulations that regulate these actions do not establish a list of documents confirming incoming transactions. It is prescribed in the internal documents of the business entity.
The receipt order is considered valid after it is signed by the accountant, and if not, by the director or the individual entrepreneur himself.
Operations for the issuance of funds from the cash register are formalized using cash receipt orders (COS).
The requirements for their preparation are no different from those established for receipt documents.
Actions of the cashier upon receipt of PKO and RKO:
- check the original signature of the chief accountant and the presence of the authorization signature of the director;
- check that all supporting documents for issuing or accepting money are properly executed;
- make sure that the necessary attachments to orders are available.
This mandatory procedure employees working at the cash register.
You can clearly see the accounting process in the 1C program in the following video:
Accounting procedure and posting examples
Before starting to work at the cash register, cashiers should carefully read their job description and a list of documents approved by the management of the enterprise that can be attached to cash orders.
IN financial statements work with the cash register is numbered score 50.
Sub-accounts can be opened for it:
- 50/1 – cash desk of the enterprise;
- 50/2 – operating cash desk of an organization (bank, transport company and others);
- 50/3 – sale and posting of monetary documents (stamps, bills, railway, air tickets).
Accounting for PKOs and RKOs occurs in their registration journal, as well as in the cash books:
- Their serial numbers are entered into the journal after the chief accountant or director signs them. It must be kept in the accounting department of the enterprise or with the director.
- A cash book is a general financial statement that records all transactions for the day (reporting period). The main requirement for it is to indicate the balance in the cash register at the end of the working day. If no transactions were carried out, then the balance will be the amount withdrawn for the previous reporting period.
There are also statements on the disbursement of funds. They must contain such mandatory details as the personal details of the person to whom payments are due, information about accrued funds, taxes paid on them and other obligatory payments, including alimony and other money collected by court decision. The total amount to be issued must also be indicated.
Typical entries for cash transactions are presented in the following table:
Accounting for cash transactions is strictly regulated by current legislation and does not tolerate negligence. If violations are detected, the subject entrepreneurial activity expect penalties from the tax office.






